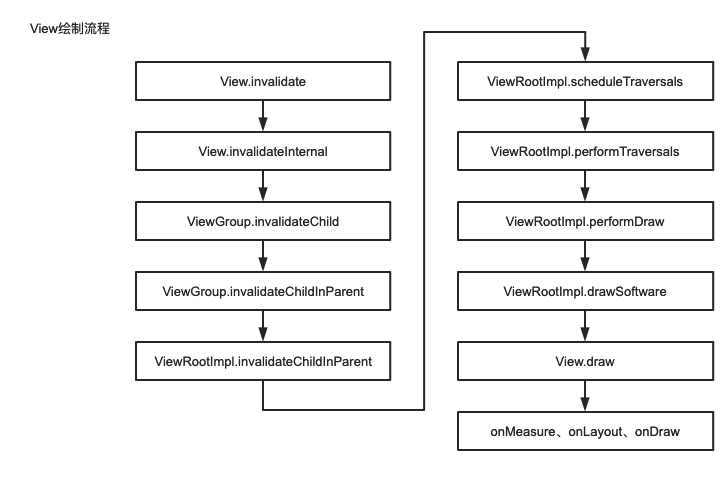
DecorView是视图的顶级View,我们添加的布局文件是它的一个子布局,而ViewRootImpl则负责渲染视图,它调用了一个performTraveals方法使得ViewTree开始
三大工作流程,然后使得View展现在我们面前。
绘制的流程概要
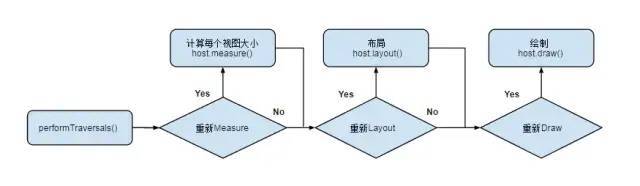
注意:这里的三个步骤是每次从根视图到最上层视图依次执行完,再进行下一步骤。
三个步骤:
测量(measure):测量视图大小。从顶层父View到子View递归调用measure方法,measure方法又回调OnMeasure。
布局(layout):确定View位置,进行页面布局。从顶层父View向子View的递归调用view.layout方法的过程,即父View根据上一步measure子View所得到的布局大小
和布局参数,将子View放在合适的位置上。绘制(draw):绘制视图。ViewRoot创建一个Canvas对象,然后调用OnDraw()。六个步骤:
- 绘制视图的背景;
- 保存画布的图层(Layer);
- 绘制View的内容;
- 绘制View子视图,如果没有就不用;
- 还原图层(Layer);
- 绘制滚动条
绘制从ViewRootImpl的performTraversals()方法开始,从上到下遍历整个视图树,每个View控件负责绘制自己,而ViewGroup还需要负责通知自己的子View进行绘制操作。
1 | private void performTraversals() { |
measure
MeasureSpec
MeasureSpec表示的是一个32位的整形值,它的高2位表示测量模式SpecMode,低30位表示某种测量模式下的规格大小SpecSize。

mode的模式分为:
- EXACTLY:对应LayoutParams中的match_parent和具体数值这两种模式。检测到View所需要的精确大小,这时候View的最终大小就是SpecSize所指定的值,
- AT_MOST :对应LayoutParams中的wrap_content。View的大小不能大于父容器的大小。
- UNSPECIFIED :不对View进行任何限制,要多大给多大,一般用于系统内部,如ListView,ScrollView
1 | public static class MeasureSpec { |
ViewGroup的measure
由于DecorView继承自FrameLayout,是PhoneWindow的一个内部类,而FrameLayout没有measure方法,因此调用的是父类View的measure方法。
View的measure
layout
View的layout流程
1 | // ViewRootImpl.java |
Layout的onLayout
1 | protected void onlayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { |
draw
1 | private void performDraw() { |
常见问题
如何在onCreate中获取View的高宽
1 | //方法1: |